The totals of each of these classifications are reported within the net assets section of the statement of financial position, along with a grand total for all net assets. The IRS provides this handy questionnaire to help you figure out exactly which parts of the tax code apply to your organization, and which form you’ll use to apply for tax-exempt status. For the most part, however, cash flow statements for non and for-profits are very similar. If you’ve dealt with for-profit cash flow statements before, this should look very familiar.
Next Up In Business
This statement allows you to determine how much money you have available to pay your expenses. You can also better understand how your organization uses the funding it receives through this document. This document allows you to be transparent about how you’re allocating your resources to donors, funders, board members, and other stakeholders. Additionally, creating a detailed Statement of Functional Expenses will help you fill out your expenses on your Form 990, simplifying the filing 5 Main Benefits of Accounting Services for Nonprofit Organizations process.
See Financial Statements Through Your Accountant’s Eyes!
It details the nonprofit’s revenue, expenses, and changes in net assets during a specific reporting period. The statement typically includes categories such as donations, grants, program service revenue, and other income sources. Nonprofit recordkeeping can get a bit challenging, so it is worth noting that accounting software exists to help nonprofits record transactions efficiently. Strong nonprofit accounting practices are the foundation for efficient financial management. Nonprofit accounting software is a bookkeeping program tailored to the needs of tax-exempt organizations.
- The IRS receives more than 70,000 applications for tax-exempt status every year, so be patient when submitting your application.
- If you don’t have enough funding to reinvest into the organization (the net assets available to your team), it will be challenging to achieve growth.
- Commercial firms that operate for-profit must meet very stringent requirements when reporting their income to the Federal government for tax purposes.
- For-profit businesses generally have the goal of maximizing revenue, keeping overhead costs low, minimizing tax liability, and generating as much net profit as possible for shareholders and owners.
- Another way to make your transition to fund accounting smooth is to choose an online donation tool that easily integrates with your accounting software.
- We also highlighted the words in the first column as they indicate the nature or type of expenses.
Free Resources
- Plus, non-cash outflows, like when you use or give away, resources you received as a donation.
- There is still a need for accounting professionals who prepare financial reports and review the financial statements to make recommendations on how to cover expenses and investments.
- In non-profit organizations, the accounts department prepares a statement of activities.
- Nonprofit accounting is essential to running a successful nonprofit organization.
- Once you’ve got your bookkeeping system setup and have started generating financial statements, the final piece of the nonprofit accounting puzzle is getting your tax obligations straight.
Additionally, you’ll need financial statements to obtain and maintain funding, grants, and other forms of support. Accurate financial statements also ensure nonprofits manage charitable resources responsibly, ethically, and according to applicable laws. While these expenses are important to your cause, they contrast with program costs, which are directly related to the initiatives that further your organization’s mission. For nonprofits, GAAP compliance means accurate fund accounting, clear reporting of restricted vs. unrestricted funds, and detailed presentation of program vs. administrative expenses. As we discussed earlier, effective nonprofit accounting involves creating thorough financial statements and reports to https://greatercollinwood.org/main-benefits-of-accounting-services-for-nonprofit-organizations/ provide an overview of your financial position.
Revenue Tracking
- Unlike for-profit businesses that exist to generate profits for their owners, nonprofit organizations exist to pursue missions that address the needs of society.
- While you may use the terms “accounting” and “bookkeeping” interchangeably, they are different yet related concepts.
- However, enlisting the expertise of a professional can streamline the process for your organization and provide valuable insights for your team.
- Nonprofit accounting is a unique process that allows nonprofit organizations to plan, record, and report on their finances.
- By the end of this guide, you’ll have the skills to confidently manage your nonprofit’s accounting needs.
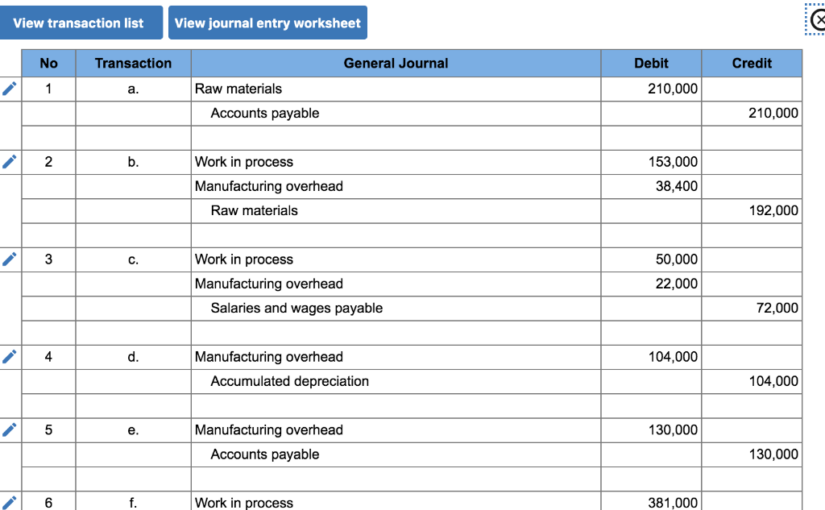
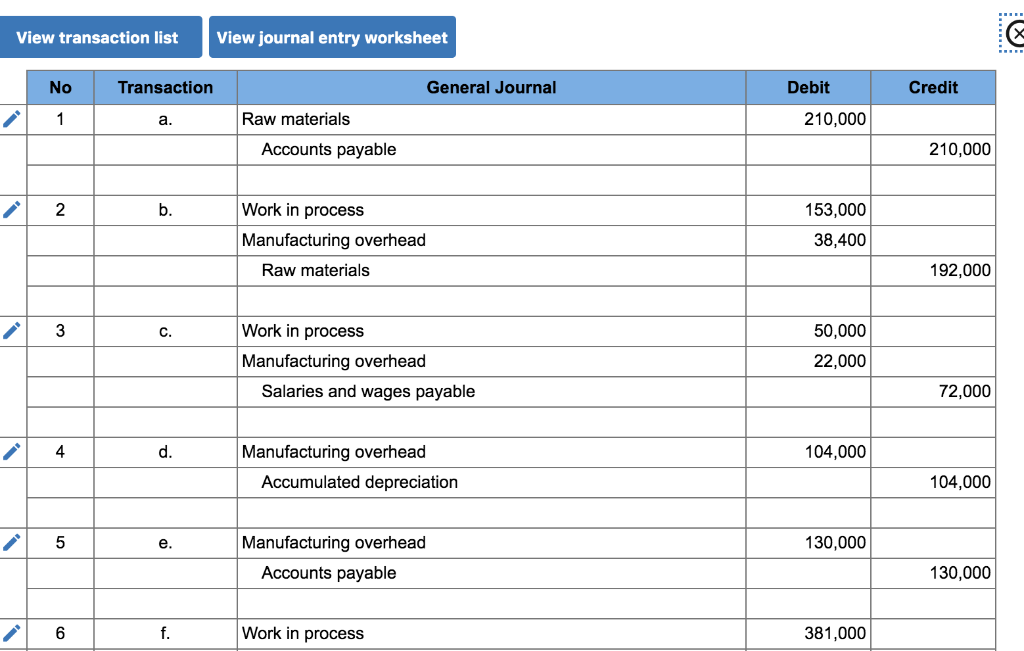
The systematic allocation of the cost of an asset from the balance sheet to Depreciation Expense on the income statement over the useful life of the asset. (The depreciation journal entry includes a debit to Depreciation Expense and a credit to Accumulated Depreciation, a contra asset account). The purpose is to allocate the cost to expense in order to comply with the matching principle.
Is Form 990 Required to be Publicly Disclosed?
This differs from regular accounting, which tracks your expenses and income. It helps ensure donor restrictions are honored and funds are used as intended. The accrual accounting method gives a more accurate picture of the organization’s financial health and helps track grants and restricted funds more effectively. Now that we’ve discussed the common challenges in nonprofit accounting let’s explore proven practices that help organizations overcome these obstacles. While every nonprofit faces unique circumstances, these fundamental strategies help build strong financial management systems that work. For-profit organizations have it simple; they just track net income from sales.
In summary, revenue management and fundraising are key aspects of nonprofit accounting. Accurate and timely recognition of revenue sources, as well as thorough documentation of fundraising efforts and donations, ensures financial transparency and compliance with accounting standards. The final option is the fund accounting method, a type of accrual accounting method specifically used for nonprofit accounting.